A groundbreaking malware distribution campaign, leveraging over 3,000 malicious YouTube videos, has recently been uncovered, marking a significant escalation in cyber crime. The operation, which has been active since 2021, primarily targets users searching for pirated software, game modifications, and cheats. Dubbed the “YouTube Ghost Network,” this covert campaign utilizes a vast network of compromised YouTube accounts to spread information-stealing malware. Its success lies in its ability to manipulate platform features and generate false trust through fabricated user engagement.
Since its inception, the campaign has grown exponentially, with its operations hitting a critical peak in 2025. Video production related to this malware scheme has tripled in the last year alone, demonstrating an alarming trend in its expansion.
A Coordinated Ecosystem of Malicious Activity
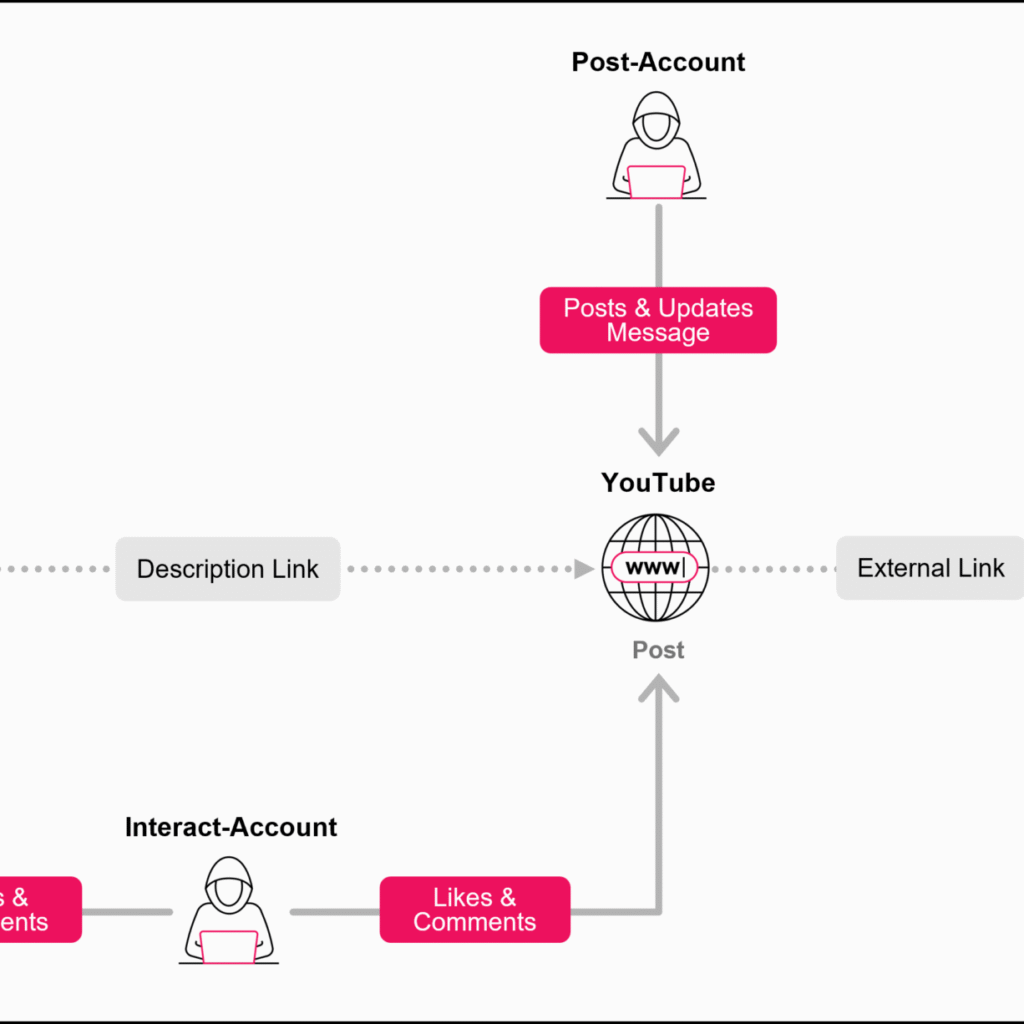
The YouTube Ghost Network operates with remarkable coordination and sophistication. The operation is powered by a network of compromised YouTube accounts, each fulfilling a specific role in the malware distribution process. These roles include:
- Video Accounts: These accounts are responsible for uploading malicious videos, often featuring pirated software or game cheats. Video descriptions or pinned comments contain embedded download links that lead users to dangerous file-sharing platforms.
- Post Accounts: These accounts maintain the appearance of a legitimate community, often posting messages with external links and archive passwords. They update these posts regularly to avoid detection and increase the likelihood that the links will be clicked by unsuspecting users.
- Interact Accounts: These accounts engage with the video content by posting positive comments, likes, and encouraging messages. This behavior generates artificial legitimacy, convincing victims that the software or cheat being advertised is safe to download and use.
The malware typically comes in the form of infostealers, which are designed to exfiltrate sensitive information, such as login credentials and personal data. One of the most prominent malware strains observed is Lumma, which remained dominant in the campaign until its disruption between March and May 2025. After this setback, the attackers switched to a new malware variant called Rhadamanthys, with the latest version, v0.9.2, demonstrating advanced evasion capabilities.
Bypassing Security Measures with Precision
What sets this campaign apart is its technical sophistication, particularly in evading detection by antivirus programs and other security solutions. The attackers have employed a variety of techniques to maintain persistence and bypass security measures:
- File Hosting on Trusted Platforms: The malicious files are hosted on well-known, legitimate platforms such as MediaFire, Dropbox, and Google Drive, which users often trust. This tactic leverages the inherent trust people have in these services to mask the malicious intent of the files.
- Large Archive Files and Password Protection: Many of the malicious files are large archives (over 189MB), which prevent automated virus scanning on platforms like Google Drive. Additionally, the files are often password-protected, making it difficult for security solutions to analyze the contents.
- Shortened URLs and Phishing Pages: The attackers often use URL shortening services to hide the true destination of their links. Additionally, they host phishing pages on Google Sites, further legitimizing their efforts and leading victims to believe they are accessing genuine content.
- Frequent Payload and Server Updates: The malware infrastructure is highly adaptable, with the attackers updating the payloads every three to four days. They also rotate command-and-control (C2) servers with each new release, further complicating detection and mitigation efforts.
Rhadamanthys and Its Evolving Threat
One of the most concerning aspects of this campaign is its evolving malware payloads. The latest strain, Rhadamanthys, has shown to be particularly adept at evading detection. Its communication with C2 servers, such as hxxps://94.74.164[.]157:8888/gateway/6xomjoww.1hj7n, enables the attackers to exfiltrate sensitive data, including usernames, passwords, and other personally identifiable information.
Interestingly, Rhadamanthys was introduced after the takedown of Lumma, demonstrating the attackers’ ability to pivot quickly and adopt new strategies. In one instance, a compromised archive contained HijackLoader as an initial payload, which then delivered Rhadamanthys and communicated with a different C2 server, hxxps://5.252.155[.]99/gateway/r2sh55wm.a56d3.
A Constantly Evolving Threat
To evade detection and bypass reputation-based security mechanisms, the attackers employ a rapid build strategy, where new variants of the malware are compiled every few days. This frequent update schedule prevents threat intelligence systems from accumulating enough data to effectively block or identify these malicious files.
For example, one of the most recent builds, compiled on September 21 and 24 of 2025, evaded detection by 57 of 63 security vendors on VirusTotal, a leading malware detection platform. The continuous updating of these malicious files makes it incredibly difficult for security solutions to keep up with the evolving nature of the campaign.
A Rising Threat with Growing Sophistication
The “YouTube Ghost Network” malware campaign is a stark reminder of the ever-evolving tactics employed by cybercriminals. Its success lies in its ability to exploit the trust users place in legitimate platforms like YouTube, Google Drive, and Dropbox. The network’s rapid growth and technical sophistication highlight the importance of staying vigilant and proactive when it comes to cybersecurity.
As the cybercriminals behind this campaign continue to refine their methods, both individual users and organizations must take steps to protect themselves. This includes being cautious when downloading software from unofficial sources, using reliable antivirus software, and ensuring that security measures, such as Windows Defender, are always active.
The YouTube Ghost Network may have started as a small-scale operation, but its growth and adaptability suggest that it could become a major threat in the coming years. Understanding how this campaign operates and taking steps to mitigate its risks is crucial to safeguarding sensitive data in today’s digital landscape.


Add a Comment